Private Shares
zrok was built to share and access digital resources. A private share allows a resource to be
accessed on another user's system as if it were local to them. Privately shared resources can only be accessed by another zrok user who has the details of your unique share. You are in control of who can access your private shares by sharing the share token.
Peer-to-peer private resource sharing is one of the things that makes zrok unique.
zrok also provides public sharing of resources with non-zrok users. Public resource sharing is limited to only resources that can be accessed over HTTP or HTTPS. private sharing works with all of the resources types that zrok supports.
Here's how private sharing works:
Peer to Peer
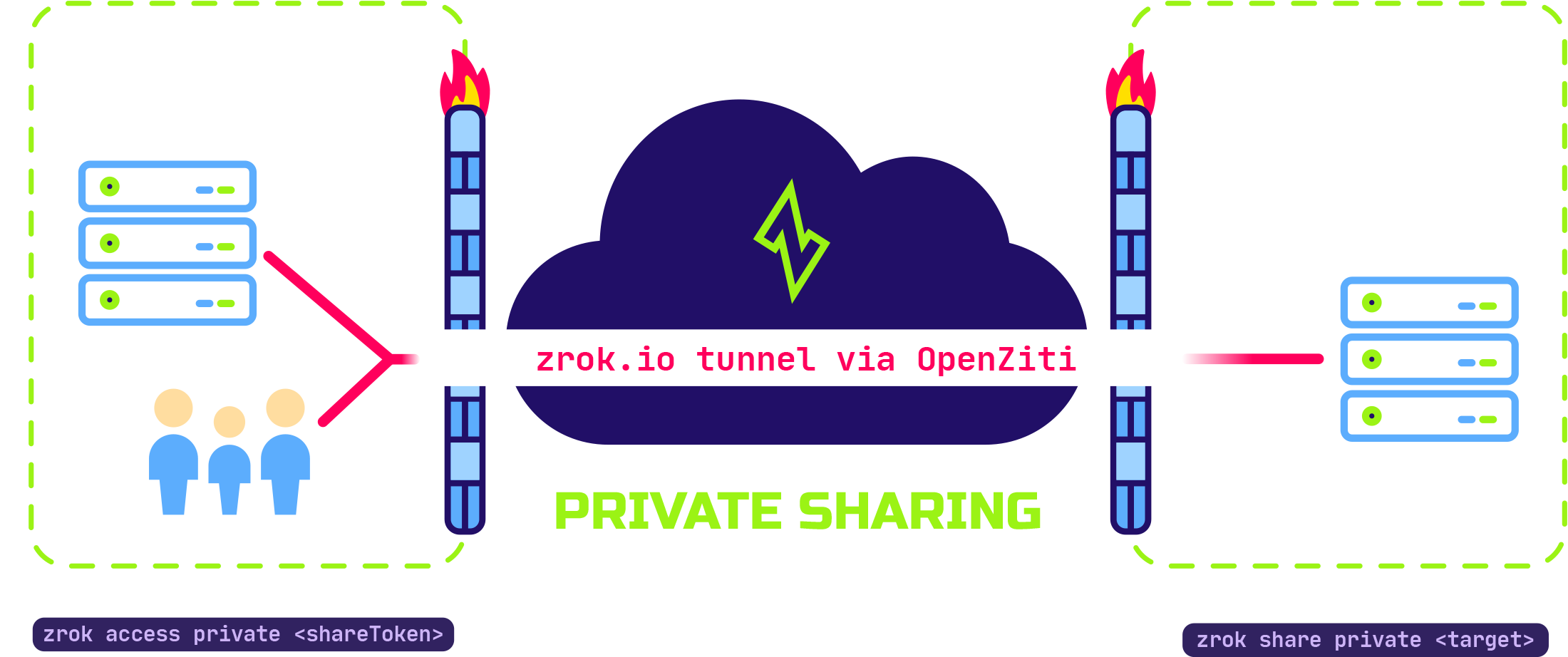
private shares are accessed using the zrok access command, and require the accessing user to have a zrok enable-d account on the same service instance where the share was created.
The private share is identified by a share token. The accessing user will use the share token, along with the zrok access command to create a local endpoint on their system, which lets them use the shared resource as if it were local to their system.
zrok does not require you to open any firewall ports or otherwise compromise the security of your local system; there is never an attack surface open to the public internet. As soon as you terminate the zrok share process, you immediately terminate any possible access to your shared resource.
The shared resource can be a development web server to share with friends and colleagues, a webhook from a server running in the cloud which has zrok running and has been instructed to access the private resource. zrok can also share files, websites, and low-level TCP and UDP network connections using the tunnel backend. What matters is that the access to the shared resource is not done in a public way, and can only be accessed by other zrok users that have access to your share token.
The peer-to-peer capabilities of zrok are an important property of the underlying OpenZiti network that zrok uses to provide connectivity between users and resources.
Creating private shares is easy and is accomplished using the zrok share private command. Run zrok share private to see the usage output and to further learn how to use the command.
Private Backend Modes
The default backend mode is proxy which targets an HTTP URL that must be reachable by the backend.
zrok share private 80
proxymode forwards requests received by the frontend to the target server (more)webmode serves a target folder as a file index web page (more)drivemode serves a target folder with WebDAV (guide)caddymode runs the built-in Caddy server with the targeted Caddyfile (example)
tcpTunnel,udpTunnelmodes forward the data payload to the target server (more)socksmode provides a SOCKS5 dynamic proxy on the private access bind port that tunnels TCP payloads to the share backend where they are forwarded to their destinations (blog)vpnmode provides a network layer tunnel between the private access and the share backend (guide)